VideometerLab多光譜成像在瑪咖摻偽定性鑒別和定量分析的應用
最近科學家利用videometerLab多光譜成像系統發表了題為Qualitative Identification and Quantitative Analysis of Maca Adulteration Based on Multispectral Imaging Technology的文章,采用多光譜成像技術, 建立了一種瑪咖與蕪菁真偽的快速無損鑒別的新方法。 主要包括瑪咖切片和瑪咖粉真偽鑒別兩部分內容; 其一是針對瑪咖切片的真偽鑒別,其二是針對瑪咖粉的真偽鑒別。
北京博普特科技有限公司是丹麥Videometer公司中國區總代理,全面負責其系列產品在中國市場的推廣。
Qualitative Identification and Quantitative Analysis of Maca Adulteration Based on Multispectral Imaging Technology
張宏蕊 劉長虹 張九凱 韓建勛 陳 穎 鄭 磊
摘要
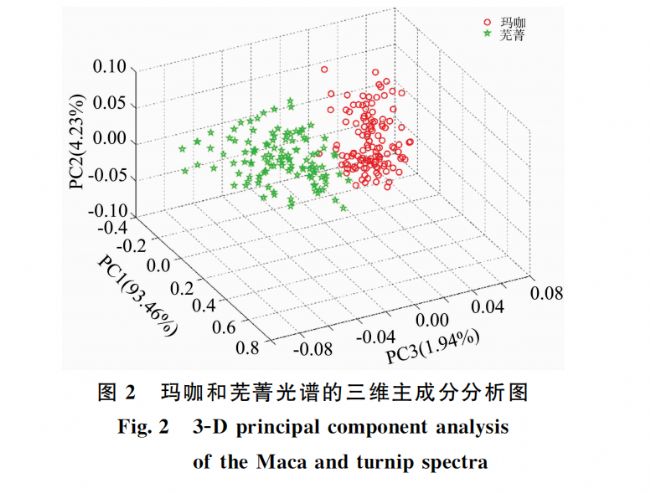
瑪咖(Lepidium meyenii Walp.)是生長在高海拔地區的十字花科獨行菜屬一年生或兩年生的草本植物, 具有豐富的營養價值和生物保健功效。 自2011年被列為新資源食品后, 瑪咖產業得到了迅速發展, 價格不斷上漲。 由于蕪菁(Brassica rapa L.)外形與瑪咖極為相似, 受經濟利益驅使, 不法商家常將蕪菁冒充瑪咖, 制成瑪咖粉、 瑪咖片和瑪咖飲品等牟取暴利, 這給瑪咖健康產業的有序發展帶來了嚴重的負面影響。 因此瑪咖的真偽鑒別是非常必要的, 但目前對于瑪咖的真偽鑒別多為傳統方法, 快速檢測方法較少。 采用多光譜成像技術, 建立了一種瑪咖與蕪菁真偽的快速無損鑒別的新方法。 主要包括瑪咖切片和瑪咖粉真偽鑒別兩部分內容; 其一是針對瑪咖切片的真偽鑒別, 通過Videometer A/S多光譜成像儀對240片瑪咖和蕪菁切片(瑪咖和蕪菁切片各120片)進行數據采集, 波長范圍在可見光區域和近紅外區域, 分別為405, 435, 450, 470, 505, 525, 570, 590, 630, 645, 660, 700, 780, 850, 870, 890, 910, 940和970 nm共19個波段, 為了有效鑒別瑪咖和蕪菁, 首先進行了主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA), 然后結合支持向量機(support vector machines, SVM), 遺傳算法優化支持向量機(genetic algorithm and support vector machine, GA-SVM)和反向傳播神經網絡(back propagation neural network, BPNN)算法建立了分析模型, 校正集與預測集的樣品數量比值為3∶1。 研究發現PCA分析可以明顯地將瑪咖和蕪菁區分, SVM模型對于瑪咖和蕪菁切片的預測正確率分別為98.33%, 100%, GA-SVM和BPNN模型對瑪咖和蕪菁切片的鑒別正確率均為100%。 其二是針對瑪咖粉的真偽鑒別, 選擇120份瑪咖粉, 向其中摻入20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 4個不同摻假水平(W/W)的蕪菁粉進行多光譜數據采集, 結合偏最小二乘(partial leastsquares, PLS)和最小二乘支持向量機(least squares-support vector machines, LS-SVM)對蕪菁的摻假比例進行了定量預測。 研究發現, PLS和LS-SVM模型對于瑪咖粉中蕪菁粉的摻入比例的預測決定系數(R2P)分別為0.992和0.994, 預測均方根誤差(RMSEP)分別為2.718%和2.675%, 相對預測誤差(RPD)分別為12.782和12.987。 相比較而言, LS-SVM模型具有更高的R2p, RPD較低的RMSEP, 對于瑪咖粉中摻入蕪菁粉比例的預測性能較好。 為瑪咖真偽的快速無損鑒別提供了一種新方法。
關鍵詞
瑪咖 蕪菁 真偽鑒別 多光譜成 無損檢測 Maca Turnip Authentic Multispec Non-destr
Abstract
Maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.), an annual or biennial herb of Brassicaceae family, grows at high altitudes and contains rich nutritional value and biohealth benefits. After being listed as a new resource food in 2011, Maca is gradually becoming familiar to the public, the Maca industry has developed rapidly and price has risen steadily. Due to the fact that the shape of turnip (Brassica rapa L.) is very similar to that of Maca, driven by economic interests, illegal businessmen often pass turnip off as Maca to make Maca powder, slices and drinks in order to make exorbitant profits, which has brought serious negative impact on the orderly development of Maca healthy industry. Therefore, the authenticity identification of Maca is very necessary, but most of methods for the authenticity identification of Maca are traditional, and there are few rapid detection methods. In this study, a new method for rapid and non-destructive identification of Maca and turnip was established by using multispectral imaging technology. The experiment mainly focuses on the authenticity identification of Maca slices and Maca powder. One is to identify the authenticity of Maca slices. A total of 240 Maca and turnip slices (120 Maca slices and 120 turnip slices, respectively) were selected to collect data by the Videometer Lab equipment, which acquired the multispectral images at 19 different wavelengths from the visual region to the lower wavelengths of the NIR region and the detailed information of the measured wavelength were 405, 435, 450, 470, 505, 525, 570, 590, 630, 645, 660, 700, 780, 850, 870, 890, 910, 940 and 970 nm. In order to identify Maca and turnip effectively, the principal component analysis (PCA) was first performed. Then the qualitative analysis model was generated using support vector machine (SVM), genetic algorithm optimization support vector machine (GA-SVM) and back propagation neural network (BPNN) algorithm, and the ratio of the the calibration set to the prediction set is 3∶1. The results demonstrated that clear differences between Maca and turnip could be easily visualized by PCA. The predictive accuracies by SVM model for Maca and turnip slices were 98.33% and 100%, respectively, and the predictive accuracies by GA-SVM and BPNN model could be as high as 100%. The other is the identification of Maca powder. 120 samples of Maca powder were selected and 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 4 different adulterated levels (W/W) of turnip powder were mixed for multispectral data acquisition, Combining partial least squares (PLS) and least squares support vector machine (LS-SVM), the adulteration ratio of turnip was quantitatively predicted. The study found that the prediction coefficient (R2P) of PLS and LS-SVM models were 0.992 and 0.994, the predicted root mean square error (RMSEP) were 2.718% and 2.675% and the relative prediction error (RPD) were 12.782 and 12.987, respectively. In comparison, the LS-SVM model had higher R2P, RPD, lower RMSEP, so it was considered to have better predictive performance for the proportion of turnip powder adulterated to Maca powder. In conclusion, the research results provide a method for the rapid and non-destructive identification of Maca authenticity.

北京博普特科技有限公司是丹麥Videometer公司中國區總代理,全面負責其系列產品在中國市場的推廣。
Qualitative Identification and Quantitative Analysis of Maca Adulteration Based on Multispectral Imaging Technology
張宏蕊 劉長虹 張九凱 韓建勛 陳 穎 鄭 磊
摘要
瑪咖(Lepidium meyenii Walp.)是生長在高海拔地區的十字花科獨行菜屬一年生或兩年生的草本植物, 具有豐富的營養價值和生物保健功效。 自2011年被列為新資源食品后, 瑪咖產業得到了迅速發展, 價格不斷上漲。 由于蕪菁(Brassica rapa L.)外形與瑪咖極為相似, 受經濟利益驅使, 不法商家常將蕪菁冒充瑪咖, 制成瑪咖粉、 瑪咖片和瑪咖飲品等牟取暴利, 這給瑪咖健康產業的有序發展帶來了嚴重的負面影響。 因此瑪咖的真偽鑒別是非常必要的, 但目前對于瑪咖的真偽鑒別多為傳統方法, 快速檢測方法較少。 采用多光譜成像技術, 建立了一種瑪咖與蕪菁真偽的快速無損鑒別的新方法。 主要包括瑪咖切片和瑪咖粉真偽鑒別兩部分內容; 其一是針對瑪咖切片的真偽鑒別, 通過Videometer A/S多光譜成像儀對240片瑪咖和蕪菁切片(瑪咖和蕪菁切片各120片)進行數據采集, 波長范圍在可見光區域和近紅外區域, 分別為405, 435, 450, 470, 505, 525, 570, 590, 630, 645, 660, 700, 780, 850, 870, 890, 910, 940和970 nm共19個波段, 為了有效鑒別瑪咖和蕪菁, 首先進行了主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA), 然后結合支持向量機(support vector machines, SVM), 遺傳算法優化支持向量機(genetic algorithm and support vector machine, GA-SVM)和反向傳播神經網絡(back propagation neural network, BPNN)算法建立了分析模型, 校正集與預測集的樣品數量比值為3∶1。 研究發現PCA分析可以明顯地將瑪咖和蕪菁區分, SVM模型對于瑪咖和蕪菁切片的預測正確率分別為98.33%, 100%, GA-SVM和BPNN模型對瑪咖和蕪菁切片的鑒別正確率均為100%。 其二是針對瑪咖粉的真偽鑒別, 選擇120份瑪咖粉, 向其中摻入20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 4個不同摻假水平(W/W)的蕪菁粉進行多光譜數據采集, 結合偏最小二乘(partial leastsquares, PLS)和最小二乘支持向量機(least squares-support vector machines, LS-SVM)對蕪菁的摻假比例進行了定量預測。 研究發現, PLS和LS-SVM模型對于瑪咖粉中蕪菁粉的摻入比例的預測決定系數(R2P)分別為0.992和0.994, 預測均方根誤差(RMSEP)分別為2.718%和2.675%, 相對預測誤差(RPD)分別為12.782和12.987。 相比較而言, LS-SVM模型具有更高的R2p, RPD較低的RMSEP, 對于瑪咖粉中摻入蕪菁粉比例的預測性能較好。 為瑪咖真偽的快速無損鑒別提供了一種新方法。
關鍵詞
瑪咖 蕪菁 真偽鑒別 多光譜成 無損檢測 Maca Turnip Authentic Multispec Non-destr
Abstract
Maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.), an annual or biennial herb of Brassicaceae family, grows at high altitudes and contains rich nutritional value and biohealth benefits. After being listed as a new resource food in 2011, Maca is gradually becoming familiar to the public, the Maca industry has developed rapidly and price has risen steadily. Due to the fact that the shape of turnip (Brassica rapa L.) is very similar to that of Maca, driven by economic interests, illegal businessmen often pass turnip off as Maca to make Maca powder, slices and drinks in order to make exorbitant profits, which has brought serious negative impact on the orderly development of Maca healthy industry. Therefore, the authenticity identification of Maca is very necessary, but most of methods for the authenticity identification of Maca are traditional, and there are few rapid detection methods. In this study, a new method for rapid and non-destructive identification of Maca and turnip was established by using multispectral imaging technology. The experiment mainly focuses on the authenticity identification of Maca slices and Maca powder. One is to identify the authenticity of Maca slices. A total of 240 Maca and turnip slices (120 Maca slices and 120 turnip slices, respectively) were selected to collect data by the Videometer Lab equipment, which acquired the multispectral images at 19 different wavelengths from the visual region to the lower wavelengths of the NIR region and the detailed information of the measured wavelength were 405, 435, 450, 470, 505, 525, 570, 590, 630, 645, 660, 700, 780, 850, 870, 890, 910, 940 and 970 nm. In order to identify Maca and turnip effectively, the principal component analysis (PCA) was first performed. Then the qualitative analysis model was generated using support vector machine (SVM), genetic algorithm optimization support vector machine (GA-SVM) and back propagation neural network (BPNN) algorithm, and the ratio of the the calibration set to the prediction set is 3∶1. The results demonstrated that clear differences between Maca and turnip could be easily visualized by PCA. The predictive accuracies by SVM model for Maca and turnip slices were 98.33% and 100%, respectively, and the predictive accuracies by GA-SVM and BPNN model could be as high as 100%. The other is the identification of Maca powder. 120 samples of Maca powder were selected and 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 4 different adulterated levels (W/W) of turnip powder were mixed for multispectral data acquisition, Combining partial least squares (PLS) and least squares support vector machine (LS-SVM), the adulteration ratio of turnip was quantitatively predicted. The study found that the prediction coefficient (R2P) of PLS and LS-SVM models were 0.992 and 0.994, the predicted root mean square error (RMSEP) were 2.718% and 2.675% and the relative prediction error (RPD) were 12.782 and 12.987, respectively. In comparison, the LS-SVM model had higher R2P, RPD, lower RMSEP, so it was considered to have better predictive performance for the proportion of turnip powder adulterated to Maca powder. In conclusion, the research results provide a method for the rapid and non-destructive identification of Maca authenticity.
Copyright(C) 1998-2025 生物器材網 電話:021-64166852;13621656896 E-mail:info@bio-equip.com